Lung Cancer Causes – Smoking
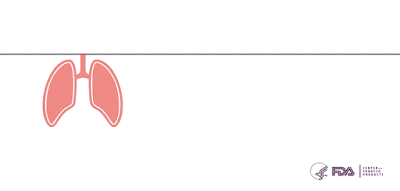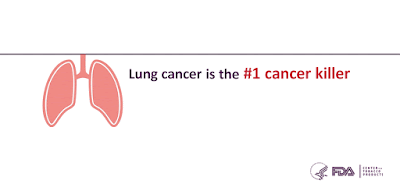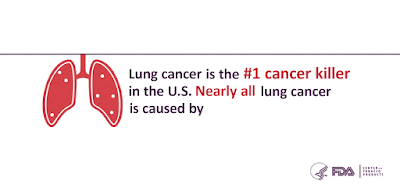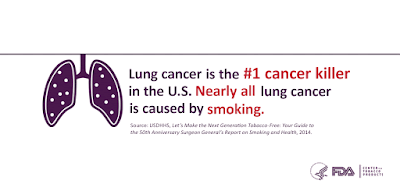
Lungcancer is the leading cancer killer of American men and women.1 Not
all people who get lung cancer are smokers, but many people who smoke
do get lung cancer. In fact, smoking is directly responsible for
approximately 90% of lung cancer deaths.
 By
far the biggest cause of lung cancer is smoking. In the U.S. alone,
there are an estimated 26.2 million men (23.5 percent) and 20.9
million women (18.1 percent) who smoke. These people are at increased
risk for lung, breast, throat, stomach, and other cancers, as well as
heart attacks, strokes, emphysema, asthma, and a variety of other
illnesses.
By
far the biggest cause of lung cancer is smoking. In the U.S. alone,
there are an estimated 26.2 million men (23.5 percent) and 20.9
million women (18.1 percent) who smoke. These people are at increased
risk for lung, breast, throat, stomach, and other cancers, as well as
heart attacks, strokes, emphysema, asthma, and a variety of other
illnesses.
Cigarette
smoking is the number one cause of lung cancer. Scientists have
reported widely on the link between cancer and smoking since the
1960s. Since then, study after study has provided more proof that
cigarette smoking is the primary cause of lung cancer.
 A
person who smokes more than one pack of cigarettes a day has a 20-25
times greater risk of developing lung cancer than someone who has
never smoked.
A
person who smokes more than one pack of cigarettes a day has a 20-25
times greater risk of developing lung cancer than someone who has
never smoked.
You
may be familiar with some of the statistics, but if you, a co-worker,
friend, or loved one is a smoker, it's worth taking another look at
what cigarettes can do to our bodies.
Sadly,
this is a disease that is easily preventable. If you don't smoke,
please don't start. It is not only an expensive and messy habit, but
it is a dangerous one. There is nothing good that can be said about
smoking. It is guaranteed to increase your risk of dying prematurely
and suffering needlessly.
Before
cigarette smoking became popular after World War I, doctors rarely,
if ever, saw patients with lung cancer. But today, lung cancer is the
leading cause of death by cancer. Over 85 percent of people with lung
cancer developed it because they smoked cigarettes.
If
you smoke cigarettes, you are at much higher risk for lung cancer
than a person who has never smoked. The risk of dying from lung
cancer is 23 times higher for men who smoke and 13 times higher for
women who smoke than for people who have never smoked. Lung cancer
can affect young and old alike.
I
will expand more on smoking and its connection to cancer at the end
of this report, but for now I want to review the other less obvious
causes.
 Cigarette smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, including more than 70 that can
cause cancer. Smoking can cause cancer almost anywhere in your body,
including the esophagus, larynx, mouth, nose, throat, trachea,
kidney, bladder, pancreas, stomach, cervix, bone marrow, and blood.
Cigarette smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, including more than 70 that can
cause cancer. Smoking can cause cancer almost anywhere in your body,
including the esophagus, larynx, mouth, nose, throat, trachea,
kidney, bladder, pancreas, stomach, cervix, bone marrow, and blood.
Some
people think only those who smoke can get lung cancer. While it is
true that smoking is the greatest risk factor for lung cancer, there
are a number of other ways that you can contract this disease.
Stopping
smoking greatly reduces your risk for developing lung cancer. After
you stop, your risk levels off. Ten years after the last cigarette,
the risk of dying from lung cancer drops by 50 percent which does not
mean, however, that risk is eliminated.And,
despite major progress over the past half-century, cigarette use
continues to be the leading cause of preventable death and disease in
the United States.
If
you are a smoker, the unfortunate fact is that you will always have a
much higher risk of developing lung cancer from any other cause than
a non-smoker, simply because you are already dealing with the
greatest risk factor: smoking. Adding other risk factors on to that
simply means you are even more at risk than you were before for
developing the disease.
Smoking
cigars and pipes also puts you at risk for lung cancer. Cigar and
pipe smokers have a higher risk of lung cancer than nonsmokers. Even
cigar and pipe smokers who do not inhale are at increased risk for
lung, mouth, and other types of cancer.



No comments:
Post a Comment